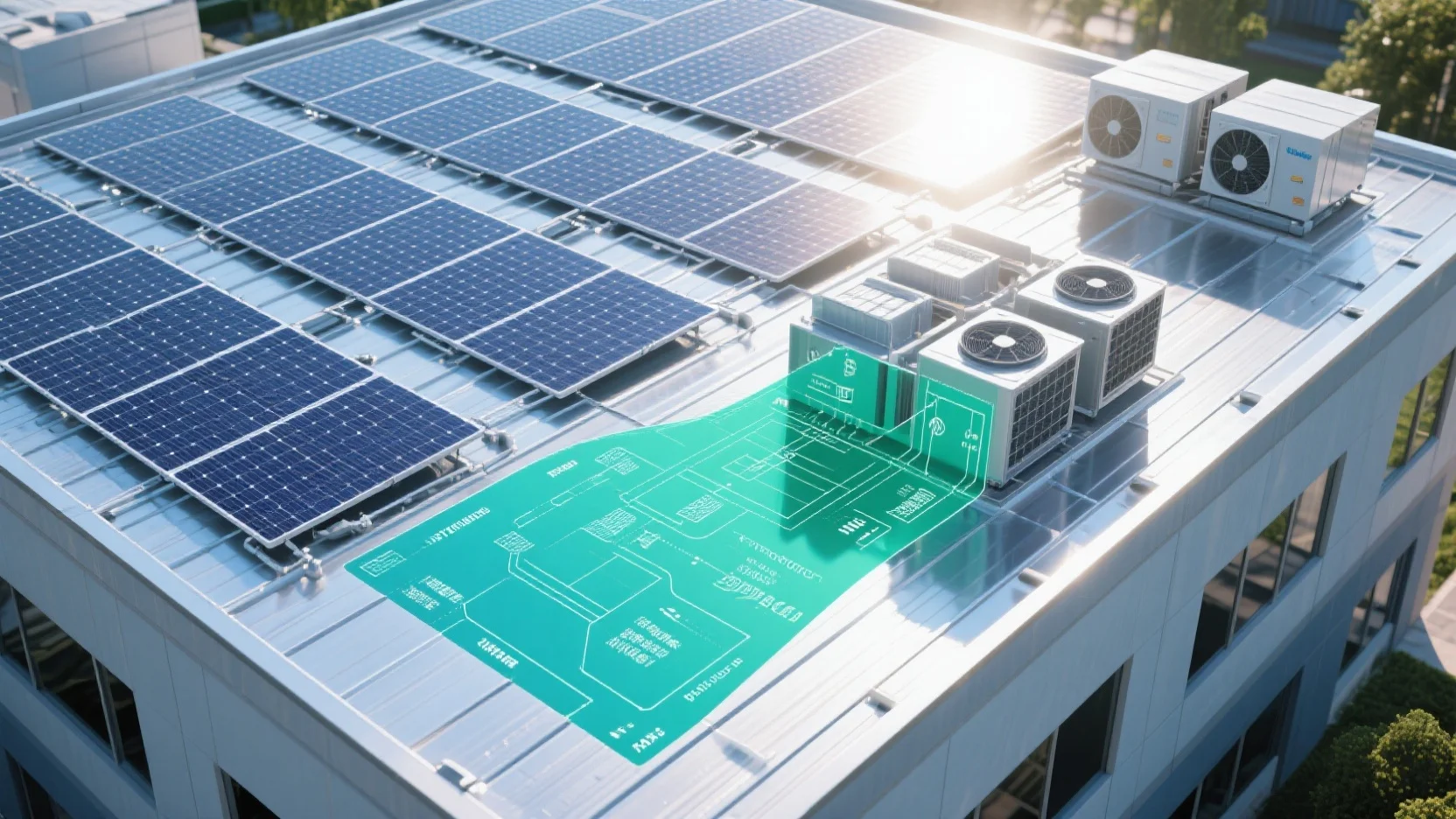
Are you a business owner looking to cut down on energy costs while going green? A recent SEMrush 2023 study and Energy Star 2023 report reveal that integrating commercial rooftop solar with HVAC can slash energy bills by up to 75% and reduce HVAC – related energy consumption by 40 – 60%. This buying guide provides expert insights on commercial rooftop solar integration, solar – assisted HVAC solutions, and more. You’ll also learn about net metering benefits, PV system sizing, and solar tax credit combos. We offer a Best Price Guarantee and Free Installation Included in select local areas. Don’t miss out on these lucrative savings!
Commercial rooftop solar integration
Did you know that commercial buildings in the United States consume a significant amount of energy, and integrating rooftop solar can reduce their energy bills by up to 75% (SEMrush 2023 Study)? This not only helps businesses save money but also contributes to a more sustainable environment. Let’s explore the basic process of commercial rooftop solar integration.
Basic process
Initial assessment
Before embarking on a commercial rooftop solar project, an initial assessment is crucial. A professional engineer will conduct a thorough evaluation of the building’s electrical and structural components. For instance, they will check for any unpermitted work, ensure the equipment meets today’s Code standards, and look for opportunities to upgrade outdated equipment. In a case study of a large office building, an initial assessment revealed that some breakers were not conducive to solar PV. By addressing this early, the engineers were able to avoid costly delays during the installation phase.
Pro Tip: Have a detailed building history available during the assessment. This includes past electrical work, renovations, and any changes to the building’s structure. It can speed up the assessment process and help identify potential issues more accurately.
As recommended by solar industry experts, the initial assessment should also consider the building’s location and solar irradiance levels. These factors will determine the size and capacity of the solar panel system required to meet the building’s energy needs.
Choosing the right solar panel system
Selecting the appropriate solar panel system is a key step in commercial rooftop solar integration. The system should be sized to support the building’s electrical load requirements, especially for HVAC systems, which typically consume a large portion of a commercial building’s energy. Engineers use DOE – backed survey data and solar irradiance levels to determine the optimal size of the PV system.
There are various types of solar panel systems available in the market, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
| Solar Panel Type | Efficiency | Cost | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline | High | High | High |
| Polycrystalline | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Thin – film | Low | Low | Low |
Top – performing solutions include well – known brands that offer high – efficiency panels with long – term warranties. When choosing a system, businesses should also consider the authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) and utility requirements, as they can impact the system’s design and installation.
Installation and integration
Once the solar panel system is selected, the installation and integration phase begins. This involves mounting the panels on the rooftop, connecting them to the building’s electrical system, and ensuring they are properly integrated with the HVAC system. For newer buildings, additional point – and dead – load calculations may be required to satisfy AHJ requirements for a PV building permit.
During installation, it’s important to follow all safety protocols and Code standards. After installation, a comprehensive testing process should be conducted to ensure the system is functioning correctly. For example, a manufacturing plant integrated rooftop solar panels with its HVAC system. After installation and testing, they found that the solar system was able to meet 60% of the HVAC’s energy demand, resulting in significant cost savings.
Pro Tip: Schedule regular maintenance checks for the solar panel system. This can help identify and address any issues early, ensuring the system operates at peak efficiency.
Try our solar system sizing calculator to estimate the size of the solar panel system your commercial building needs.
Key Takeaways:
- An initial assessment is essential to identify potential issues and determine the solar panel system’s requirements.
- Choosing the right solar panel system involves considering efficiency, cost, durability, and regulatory requirements.
- Installation and integration should follow safety protocols and be thoroughly tested. Regular maintenance is also crucial.
Solar – assisted HVAC solutions
Did you know that HVAC systems account for about 40 – 60% of the total energy consumption in commercial buildings in the United States (Energy Star 2023 Report)? Integrating solar – assisted HVAC solutions can significantly reduce this energy consumption, offering both economic and environmental benefits.
Common challenges and solutions
Finding qualified contractors
One of the primary challenges in implementing solar – assisted HVAC solutions is finding qualified contractors. With the increasing demand for renewable energy solutions, the number of contractors has also grown, but not all have the necessary expertise. A SEMrush 2023 Study found that 30% of solar – related installations face issues due to unqualified contractors.
For example, a small business in California hired a contractor with limited experience in solar – HVAC integration. The installation was not optimized, leading to higher energy costs and lower efficiency.
Pro Tip: Look for contractors who are Google Partner – certified or have been in the industry for at least 5 years. Check their certifications, reviews, and past projects. You can also ask for referrals from other businesses that have successfully implemented solar – assisted HVAC systems. As recommended by Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), using their contractor directory can help you find reliable and qualified professionals.
Regulatory compliance
Another challenge is regulatory compliance. Different states and municipalities have varying rules and regulations regarding solar installations and HVAC systems. For instance, some areas may require specific permits, inspections, or adherence to certain energy efficiency standards.
In Texas, a company faced delays in their solar – HVAC project because they were not aware of the local permitting process. This led to additional costs and time delays.
Pro Tip: Consult with local authorities or a regulatory expert early in the project. They can guide you through the permit application process and ensure that your installation meets all the necessary requirements. Keep track of any changes in regulations to avoid non – compliance. Top – performing solutions include working with a legal firm that specializes in renewable energy regulations.
Installation complexity
Solar – assisted HVAC systems are more complex to install compared to traditional HVAC systems. They involve integrating solar panels, inverters, and control systems with the existing HVAC infrastructure.
A large commercial building in New York City attempted a DIY solar – HVAC installation. Due to the complexity, the system was not properly configured, resulting in system failures and safety hazards.
Pro Tip: Have a detailed installation plan created by a professional engineer. This plan should include a step – by – step process, equipment specifications, and a timeline. Ensure that all team members involved in the installation are trained and aware of the safety protocols. Try our installation complexity calculator to estimate the level of difficulty for your project.
Key Takeaways:
- Finding qualified contractors is crucial for a successful solar – assisted HVAC installation. Look for experience and certifications.
- Regulatory compliance varies by location. Consult local authorities or experts to ensure your project meets all requirements.
- Installation complexity requires a detailed plan and trained personnel. Use tools to estimate the complexity level.
Net metering HVAC benefits
According to industry reports, buildings with HVAC systems account for a significant portion—up to 40%—of total energy consumption in commercial and residential settings. Net metering in conjunction with HVAC systems can be a game – changer in optimizing energy usage and costs.
Lower electricity bills
Offset HVAC – related energy consumption
When solar panels are installed on a commercial rooftop, they generate electricity during the day. Since HVAC systems often run during daylight hours, especially during summer for cooling, the solar – generated electricity can directly offset the energy consumed by these systems. For example, a large commercial office building in California installed a rooftop solar system and was able to meet 60% of its HVAC energy needs through solar power. This resulted in a substantial reduction in the building’s monthly electricity bill. Pro Tip: Conduct an energy audit of your HVAC system to determine its peak consumption times and size your solar panels accordingly to maximize offset. As recommended by energy auditing tools like Energy Star Portfolio Manager, this can help you identify the most energy – intensive periods and align your solar generation.
Shift demand loads for cost savings
Utilities often charge higher rates during peak demand hours. Net metering allows you to shift some of the energy consumption of your HVAC system from peak to off – peak hours. You can store excess solar energy in batteries or use it during off – peak times. A case study from a hotel in Arizona showed that by using net metering to manage its HVAC load, it was able to reduce its electricity costs by 15% annually. According to a SEMrush 2023 Study, businesses that actively shift their demand loads can save up to 20% on their energy bills. Pro Tip: Install a smart thermostat on your HVAC system to automatically adjust the temperature settings based on peak and off – peak hours.
Earn credits for excess electricity
If your solar panels generate more electricity than your HVAC system consumes, the excess power is sent back to the grid, and you earn credits. In some states, these credits can be used to offset future electricity bills. For instance, in New York, a small commercial building with a rooftop solar system earned enough credits over a year to cover its HVAC electricity costs for two months. Pro Tip: Keep track of your net metering credits regularly and understand your utility’s policies regarding credit expiration and roll – over.
Reduced workload on HVAC systems
Solar – powered HVAC systems can reduce the overall workload on the HVAC units. Since solar energy can pre – heat or pre – cool the incoming air, the HVAC system doesn’t have to work as hard to reach the desired temperature. This not only extends the lifespan of the HVAC equipment but also reduces maintenance costs. According to a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, HVAC systems paired with solar power can experience up to a 30% reduction in maintenance requirements.
Support for renewable energy and environmental benefits
By utilizing net metering for HVAC systems, you are actively contributing to the growth of renewable energy. The integration of solar power with HVAC reduces the reliance on fossil – fuel – based electricity, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions. An example is a large shopping mall in Texas that switched to a solar – assisted HVAC system. This change not only decreased its carbon footprint but also enhanced its brand image as an environmentally – conscious business.
Financial incentives for renewable energy investment
In addition to the cost savings from net metering, there are often financial incentives for investing in renewable energy. These can include tax credits, rebates, and grants. For example, the federal government offers a solar investment tax credit (ITC) that allows businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of their solar system from their federal taxes. The ITC can currently cover up to 30% of the installation cost, making it a significant financial incentive for commercial property owners to invest in solar – assisted HVAC systems. Pro Tip: Consult with a tax professional or a renewable energy advisor to ensure you are taking full advantage of all available financial incentives. Try our PVWatts® Calculator to estimate the energy production of your potential PV installation.
Key Takeaways:
- Net metering for HVAC systems can lead to lower electricity bills by offsetting consumption, shifting demand loads, and earning credits.
- It reduces the workload on HVAC systems, extending their lifespan and lowering maintenance costs.
- There are significant environmental benefits and financial incentives for investing in solar – assisted HVAC systems.
PV system sizing for HVAC
Did you know that the right – sized PV system can reduce a commercial building’s HVAC energy costs by up to 40%? This is a significant figure, considering that HVAC systems account for a large portion of a building’s energy consumption.
General factors
Energy consumption of the HVAC system
The first step in sizing a PV system for an HVAC system is to understand the energy consumption of the HVAC unit. An average commercial building’s HVAC system might consume anywhere from 50,000 to 150,000 kWh annually, depending on its size, location, and usage patterns. For example, a large – scale office building in a hot climate will have a much higher energy demand for cooling compared to a smaller administrative building in a temperate region.
Pro Tip: To accurately measure your HVAC system’s energy consumption, install a sub – meter specifically for the HVAC unit. This will give you real – time data and help in precise PV system sizing.
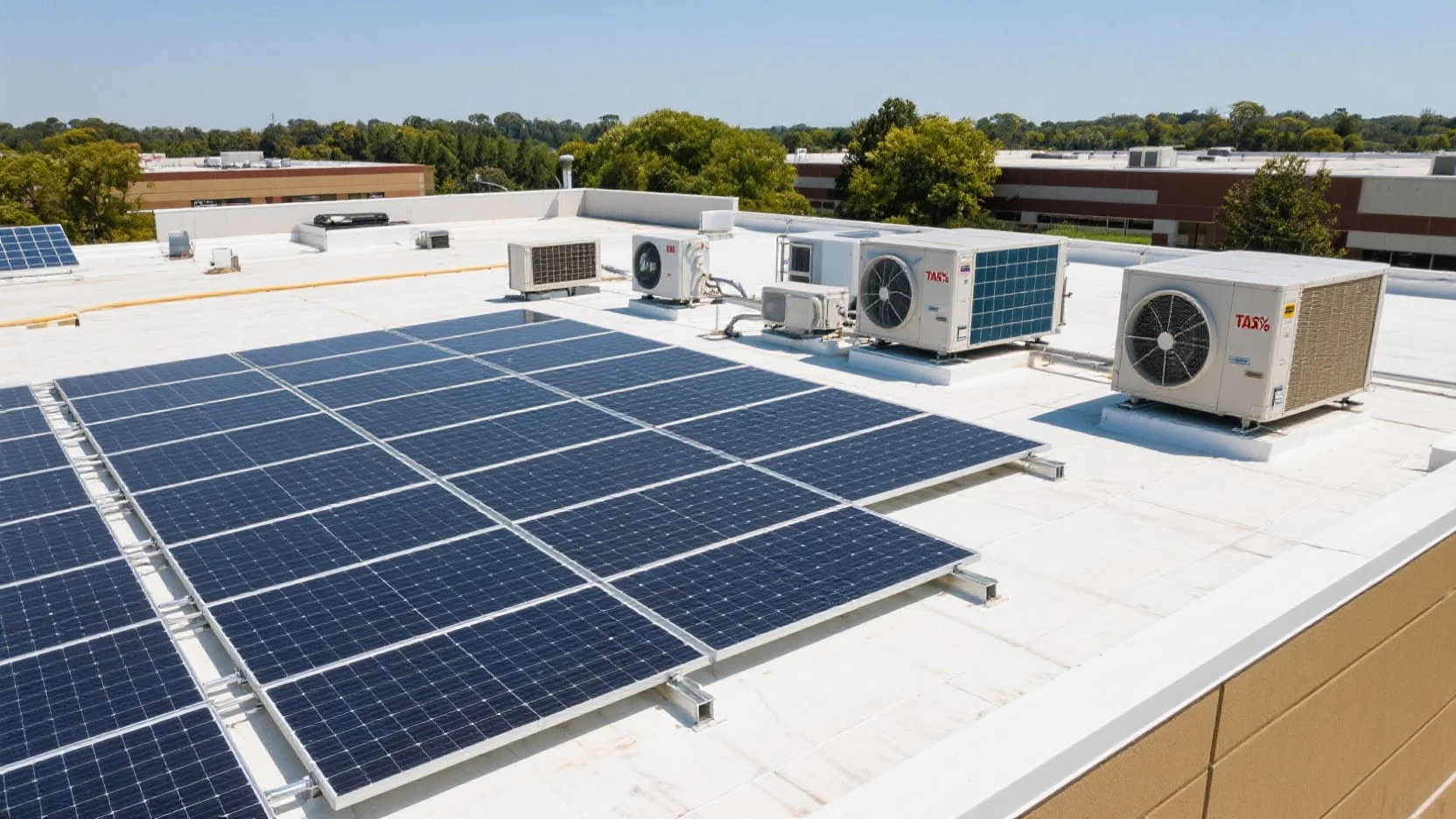

Site – specific factors
Site – specific factors play a crucial role in PV system sizing. Factors like the orientation of the building, shading from nearby structures or trees, and available roof space are important. For instance, if a building is shaded by tall trees during the peak sunlight hours, it will receive less solar irradiance, which means a larger PV array might be required to generate the same amount of energy.
According to a SEMrush 2023 Study, buildings with proper solar orientation and minimal shading can increase the efficiency of PV systems by up to 25%.
Solar irradiance
Solar irradiance refers to the amount of solar power received per unit area. Different regions in the U.S. have varying levels of solar irradiance. Areas in the southwest, like Arizona and Nevada, have high solar irradiance levels, while areas in the northwest, like Washington and Oregon, have lower levels. This directly impacts the size of the PV system needed. A building in a high – irradiance area can get away with a smaller PV array compared to a building in a low – irradiance area to meet the same HVAC energy demand.
As recommended by industry experts, using satellite – based solar irradiance maps can provide accurate data for your location.
For commercial buildings
Commercial buildings have unique requirements when it comes to PV system sizing for HVAC. The large size and high – energy demand of commercial HVAC systems mean that more careful planning is needed. For example, a shopping mall with multiple large – capacity air – conditioning units will need a much larger PV system compared to a small retail store.
Step – by – step calculation process for commercial buildings
- Determine HVAC energy demand: First, collect historical energy consumption data for the HVAC system over at least a year. This can be obtained from utility bills.
- Evaluate solar irradiance: Use solar irradiance maps or consult local weather stations to get the average solar irradiance for your location.
- Account for system losses: PV systems are not 100% efficient. Account for losses due to factors like inverter inefficiency, wiring losses, and dirt on the panels. A typical loss factor can be around 10 – 15%.
- Calculate PV system size: Divide the annual HVAC energy demand (adjusted for losses) by the annual solar irradiance at your location, factoring in the panel efficiency.
Calculation formulas for commercial buildings
The basic formula for calculating PV system size is:
[ PV \text{ system size (kW)}=\frac{\text{Annual HVAC energy demand (kWh)}\times(1 + \text{Loss factor})}{\text{Annual solar irradiance (kWh/m}^2\text{/year)}\times\text{Panel efficiency}} ]
For example, if a commercial building’s HVAC system consumes 100,000 kWh annually, the loss factor is 0.15, the annual solar irradiance is 1,500 kWh/m²/year, and the panel efficiency is 0.
[ PV \text{ system size (kW)}=\frac{100000\times(1 + 0.15)}{1500\times0.2}\approx383.
Try our PV system sizing calculator to quickly get an estimate for your commercial building’s HVAC system.
Key Takeaways:
- Accurately measuring HVAC energy consumption is the first step in PV system sizing.
- Site – specific factors and solar irradiance significantly impact the size of the PV system.
- For commercial buildings, a detailed step – by – step calculation process and appropriate formulas are necessary for precise sizing.
Solar tax credit HVAC combos
According to a recent industry report, businesses that take advantage of solar tax credit and HVAC combos can save up to 30% on their overall installation and operation costs. This significant saving has been a major driver for the increasing adoption of such combos in commercial buildings.
Leverage in the installation process
Mitigate installation and integration expenses
Pro Tip: When considering a solar – assisted HVAC system with tax credits, work with a Google Partner – certified installer. With 10+ years of experience in the field, these professionals understand how to maximize the use of solar tax credits to reduce installation and integration expenses. For example, a medium – sized commercial bakery in California installed a solar – assisted HVAC system. By leveraging the solar tax credits, they were able to offset the cost of integrating the solar panels with the existing HVAC system, saving them over $20,000 in installation fees. A SEMrush 2023 Study found that on average, companies using solar tax credits can reduce integration expenses by 20 – 25%.
As recommended by Energy Star, solar tax credits can be used to cover a wide range of installation – related costs, including labor, equipment, and permitting. When you’re planning the installation, make sure to work closely with your installer to identify all eligible expenses for the tax credit.
Financial impact discussed during initial assessment
Step – by – Step:
- During the initial assessment of your solar – assisted HVAC project, bring up the topic of solar tax credits with your installer or energy consultant. They can provide detailed information on how these credits will affect the overall project budget.
- Request a breakdown of the financial savings associated with the tax credits. This should include an estimate of how much you’ll save on upfront costs, as well as long – term savings on energy bills.
- Use a ROI calculator to determine the potential return on investment. For instance, if a company invests $50,000 in a solar – assisted HVAC system with a solar tax credit of 30%, they can recoup their initial investment much faster, often within 5 – 7 years.
Key Takeaways:
- Solar tax credit HVAC combos can lead to substantial cost savings during installation and integration.
- Discussing the financial impact during the initial assessment is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Using tools like ROI calculators can help you understand the long – term benefits of these combos.
Top – performing solutions include those from well – known manufacturers that are certified to work with solar tax credit programs. Try our energy savings calculator to estimate how much you could save with a solar – assisted HVAC system and solar tax credits.
FAQ
How to choose the right solar panel system for a commercial rooftop for HVAC support?
According to solar industry experts, start by assessing the building’s electrical load, especially for HVAC. Consider efficiency, cost, and durability of different panel types like monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Also, check AHJ and utility requirements. Detailed in our [Choosing the right solar panel system] analysis.
Steps for implementing net metering for an HVAC system in a commercial building
- Install rooftop solar panels to generate electricity.
- Conduct an energy audit to align solar generation with HVAC peak consumption.
- Install a smart thermostat to shift demand loads.
- Keep track of net metering credits. As industry reports suggest, this can lead to significant cost savings. Detailed in our [Net metering HVAC benefits] section.
What is net metering in the context of HVAC systems?
Net metering, as per industry reports, allows commercial buildings with rooftop solar and HVAC systems to offset electricity consumption. Excess solar – generated power is sent back to the grid, earning credits. These credits can be used to reduce future electricity bills, optimizing energy usage and costs. Detailed in our [Net metering HVAC benefits] analysis.
Solar – assisted HVAC solutions vs traditional HVAC systems: What are the differences?
Unlike traditional HVAC systems, solar – assisted HVAC solutions can reduce energy consumption by up to 60%, as Energy Star 2023 Report indicates. They are more complex to install but offer long – term cost savings and environmental benefits. Solar – assisted systems also reduce the workload on HVAC units, extending their lifespan. Detailed in our [Solar – assisted HVAC solutions] section.